The period 2020 to 2023 has been unique in history. Many businesses have seen a double recession: first the covid pandemic, then the Ukraine-war led inflation and interest rate peak. The two recessions are qualitatively different: the first was caused by massive behavioural changes and ameliorated by government actions to cushion it, the second is caused by government actions to squeeze borrowers and strangle inflation.
A good thing about having a long-standing “evidence based” approach is that PIMS is rich, uniquely so, in time series data. This allows us to draw on the lessons learned from past recessions and recoveries.
Bold behaviour is the way to maintain profitability through the bad times and achieve sustainable growth during recovery. Our evidence distinguishes between:
- ‘Good costs’, which should be increased and intensified during recession.
- ‘Bad costs’ which need to be pruned hard in recession, and
- ‘It depends’ costs where the right actions depend on your circumstances when recession began.
We also distinguish between recessions pre and post 2000. The latest recession resembles those of the last century in that it is driven by high inflation and interest rates.
The evidence on ‘good costs’
The most pointed ‘good cost’ is the one that most often gets cut in a recession: marketing. Figure 1 shows that ‘spenders’ who increase marketing do not suffer during recession, while their profits increase dramatically faster once recovery starts, far more than ‘cutters’. Furthermore, ‘spenders’ gain market share much faster in recovery.
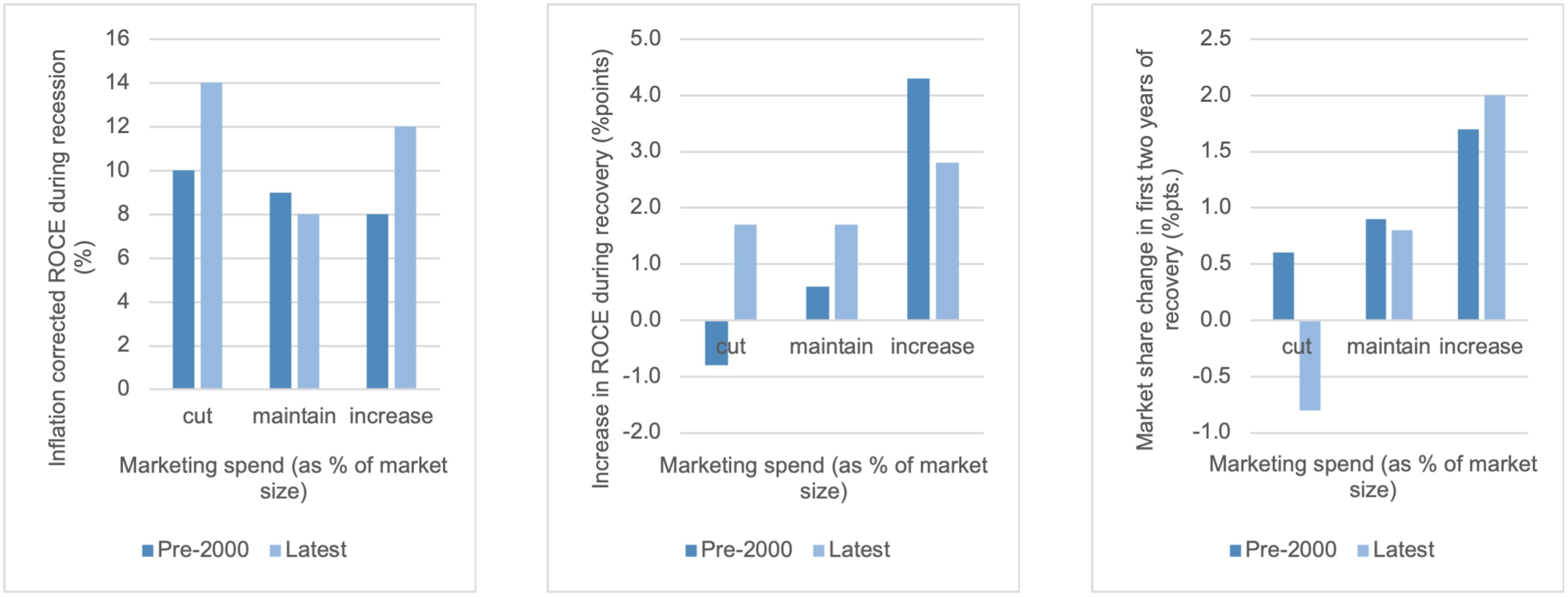
Figure 1: Upping marketing in a recession helps profit recovery and share gain - and recently without hurting profits even during the bad time
For marketing to be effective, it must be based on a sound customer proposition. If you, in your customers’ eyes, provide better (and improving) value for money than competitors, this pays off in better profits and growth.
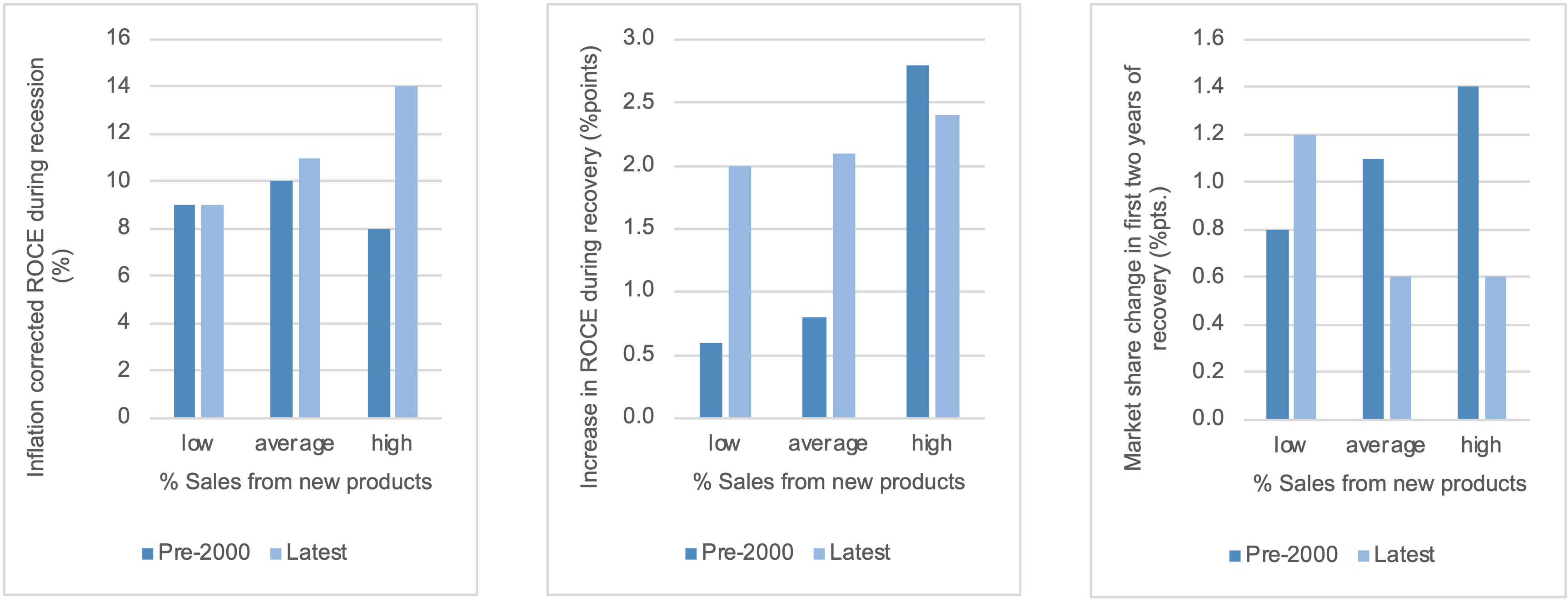
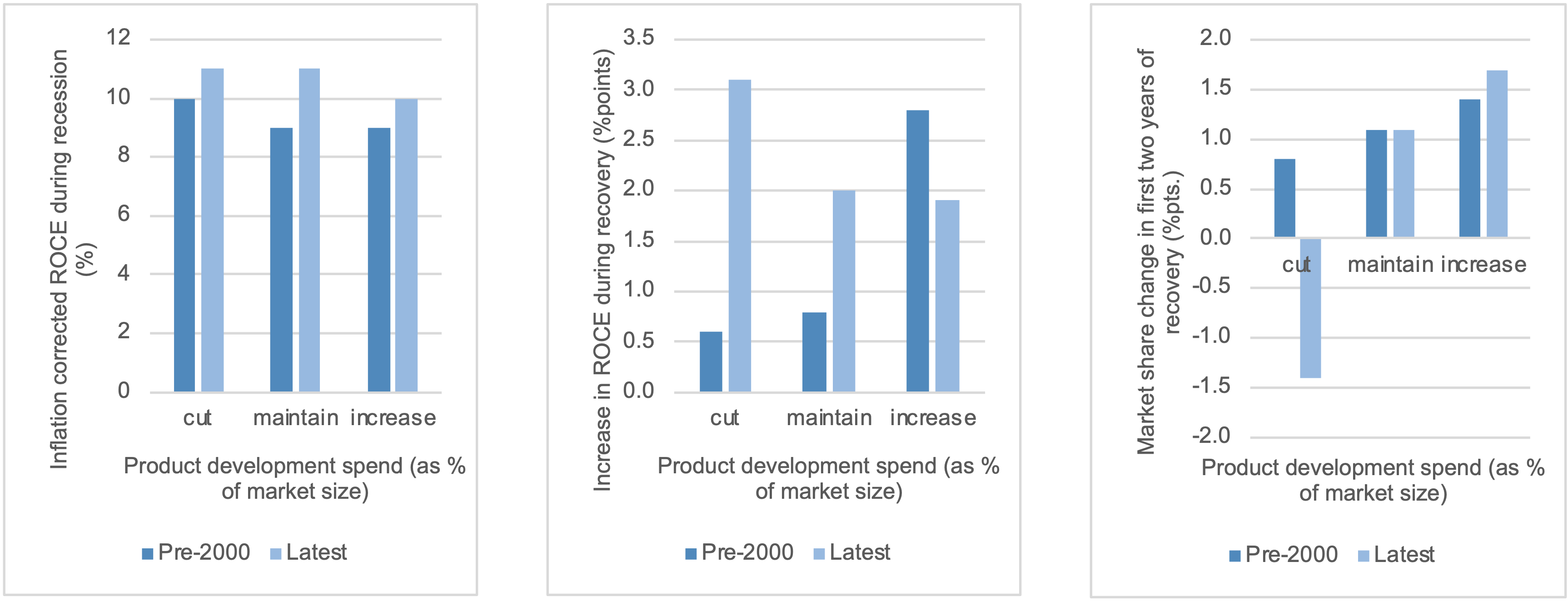
Figure 2: new products now have a positive effect on profits even during the recession - but tend to be more about margin improvement than share gain
That said, new products are the result of past Research & Development; in a recession R&D gets focussed on quick wins to the customer value proposition. This means little or no observed adverse profit effect during the downturn and very positive share gain in recovery (though less profit recovery in recent years).
Bad costs
Investing in new fixed assets during recession, intended to improve cost competitiveness and productivity, does not usually bring positive benefits. If anything, the opposite is the case. This is because the supposed benefits of new assets tend to get “competed away” in the form of lower prices and profit margins in an attempt to fill capacity. Other ‘Bad costs’ are high working capital, high manufacturing costs and high administrative overheads.
Understanding when it depends
Cutting output capacity during recession (and, thus, people and costs) may seem a very appropriate strategy. For market leaders, howe§ver, cutting capacity holds back improvement during recovery.
Outsourcing is a rapidly increasing trend, partly to allow businesses to concentrate on their core competencies and partly to generate cost savings and efficiencies. So, what better time to outsource more of your services than in a recession? ‘It depends’ on your market position and whether your priority for recovery is profit or share gain.
Beware the panacea!
The general PIMS findings are a guide. They are not a panacea for all businesses in all circumstances. Indeed, for some, opposite “rules” apply. For example, for one business the best strategy in recession was to cut back on product launches and to increase investment in overheads to improve the quality of interaction with customers and suppliers.
In recession, the best way to ensure that you adopt the right strategies for your business is to determine which strategies have proved successful for businesses analogous to your own (e.g. PIMS ‘look-alikes’).
Businesses that face this recession head on by using evidence to understand the likely market reaction, and then devising strategies to stand out from the crowd, will emerge the winners.
Bold strategies are required for recession
| Increase “good costs” | Cut “bad costs” | It depends |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Please click here to download the article as a PDF.